
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, an information security policy is a safeguard, fortifying organizations against the ever-growing threat of cyber vulnerabilities. This document outlines the strategies and protocols to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information.
It defines the scope, assigns responsibilities, and establishes risk management and access control guidelines. Beyond compliance and legal considerations, the policy fosters a culture of awareness through training programs and incident response protocols.
Crafting an effective policy involves periodic reviews, updating procedures, and addressing the challenges inherent in implementation. A robust information security policy shields against cyber threats and builds trust among stakeholders, making it a cornerstone for organizational resilience.
The Importance of Information Security Policies
In today’s interconnected world, where data breaches and cyber threats loom, information security policies play a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive information. These policies establish a framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with the storage and transmission of data.
These policies assist companies in safeguarding their assets and upholding the confidence of their stakeholders, partners, and customers by providing standards and processes for data access, encryption, and incident response. Information security policies also ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, reducing the likelihood of legal penalties and reputational damage.
Essentially, they serve as a proactive defense mechanism against evolving cyber threats, emphasizing the critical importance of prioritizing data security in today’s digital landscape.
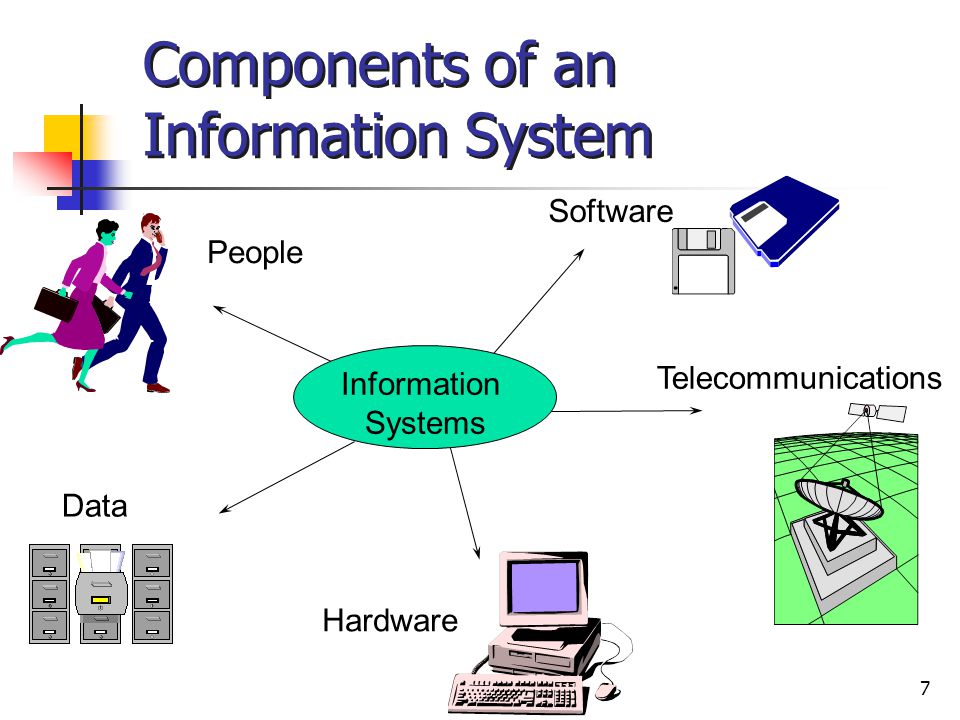
Components of an Information Security Policy
An information security policy comprises essential components that form the backbone of an organization’s cybersecurity framework. First and foremost, it delineates the policy’s scope and purpose, defining its application’s boundaries.
Roles and responsibilities are clearly outlined, assigning accountability for implementing and enforcing security measures. Risk management strategies, including risk assessment and mitigation protocols, help identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Access control mechanisms regulate user permissions, limiting unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Additionally, incident response procedures outline steps to be taken during a security breach, ensuring swift and effective resolution. Together, these components create a comprehensive and proactive approach to safeguarding digital assets and maintaining the integrity of organizational data.
Definition and Scope
In an information security policy, the section on definition and scope sets the groundwork for the entire document. It precisely defines the terms and terminology used throughout the policy, ensuring clarity and understanding among stakeholders.
Additionally, it outlines the boundaries and applicability of the policy, specifying the types of data and information systems covered. This section is the starting point for establishing a robust framework for safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating cyber risks within the organization.
Roles and Responsibilities
The section on Roles and Responsibilities within an Information Security Policy delineates the individuals or groups accountable for maintaining an organization’s security posture. It assigns specific duties and obligations to stakeholders at various levels, including management, IT personnel, and end-users.
Management is typically tasked with setting strategic direction and allocating resources for security initiatives. IT personnel are responsible for implementing and managing technical safeguards, while end-users must adhere to established security protocols and report suspicious activities.
By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, the policy ensures accountability, fosters collaboration, and promotes a culture of security awareness throughout the organization, enhancing its resilience against cyber threats.
Risk Management
Risk management is a cornerstone of any robust information security policy. It involves systematically identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to an organization’s information assets and operations. This process begins with identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise data confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
Next, risks are assessed based on their likelihood and potential impact. Strategies are then developed to mitigate or eliminate these risks, including implementing security controls, transferring risk through insurance, or accepting certain risks as unavoidable. By proactively managing risks, organizations can strengthen their security posture, minimize potential harm, and ensure the continuity of their operations in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats.

Access Control
Access control is a fundamental component of an effective information security policy, governing who has permission to access specific resources within an organization’s network or information systems. It involves implementing mechanisms and protocols to authenticate users and enforce authorized access levels.
Access control measures may include passwords, biometric authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), and encryption. Access control helps prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats by limiting access to only those who require it to perform their job functions.
Additionally, it enables organizations to enforce compliance with regulatory requirements and protect sensitive information from malicious actors. Effective access control is essential for maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical data assets.
Creating an Effective Information Security Policy
Crafting an effective information security policy requires careful consideration and strategic planning. It involves conducting thorough risk assessments, understanding organizational goals and objectives, and aligning security measures with industry best practices.
Clear guidelines and procedures must be established to address potential threats and vulnerabilities while promoting a culture of security awareness among employees. To guarantee that the policy stays current and adaptable to changing cyber threats, it is imperative to conduct regular reviews and modifications.
Conducting Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment is critical to developing an effective information security policy. It involves identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and the likelihood of security incidents occurring within an organization’s environment. Risk assessments help prioritize security efforts by evaluating the impact of various threats on business operations and data integrity.
By understanding the potential risks, organizations can develop targeted mitigation strategies and allocate resources effectively to address the most significant threats. Regular risk assessments ensure that security measures remain aligned with evolving threats and changes in the organizational landscape, enabling proactive protection of sensitive information and systems against cyber threats.

Establishing Clear Guidelines
Establishing clear guidelines is paramount to developing an effective information security policy. These guidelines outline specific rules and procedures that govern an organization’s handling, storage, and transmission of sensitive information.
Clarity in these guidelines ensures that employees understand their data security and privacy responsibilities. It also helps standardize practices across different departments and teams, fostering consistency and alignment with regulatory requirements.
Clear guidelines should address data classification, acceptable use of technology resources, password management, and incident reporting procedures. By providing a roadmap for compliance and accountability, clear guidelines empower employees to contribute to the organization’s overall security posture while minimizing the risk of data breaches and cybersecurity incidents.
Implementing Monitoring Mechanisms
Implementing monitoring mechanisms is essential for maintaining the integrity and security of an organization’s information systems. These mechanisms involve continuously surveilling and analyzing network traffic, system logs, and user activities to detect unauthorized or suspicious behavior. Monitoring tools and technologies provide real-time alerts and notifications to IT security personnel, enabling swift responses to potential threats or breaches.
Additionally, monitoring helps organizations identify patterns and trends in cyber threats, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate future risks. By implementing robust monitoring mechanisms, organizations can enhance their overall security posture, reduce the impact of security incidents, and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or exploitation.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Compliance with regulatory requirements and legal standards is paramount to ensuring the effectiveness of an organization’s information security policy. This entails adhering to laws, regulations, and industry standards relevant to data protection and privacy. Organizations must stay abreast of evolving compliance requirements and incorporate them into their security frameworks to mitigate legal risks and liabilities. Compliance efforts often involve:
- We are implementing controls and safeguards to safeguard sensitive data.
- We are conducting regular audits and assessments.
- We are maintaining documentation to demonstrate adherence to regulatory mandates.
By prioritizing compliance and legal considerations, organizations can instill trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders while avoiding penalties, fines, and reputational damage associated with non-compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Training and Awareness Programs
Programs for awareness and training are essential parts of a successful information security strategy. These programs educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as identifying phishing attempts, creating strong passwords, and safeguarding sensitive information.
By increasing awareness of potential threats and promoting a culture of security consciousness, organizations empower employees to become proactive defenders against cyber risks. Regular training sessions, workshops, and simulated phishing exercises help reinforce security protocols and ensure that employees remain vigilant in protecting the organization’s digital assets. Ultimately, investing in training and awareness programs strengthens the organization’s overall security posture.
Incident Response and Reporting
Incident response and reporting procedures are integral to an organization’s information security policy. These protocols outline the steps to be taken during a security incident, such as a data breach or cyberattack. Prompt reporting of incidents allows for swift containment and mitigation of potential damages, minimizing the impact on operations and data integrity.
Clear communication channels and escalation procedures ensure that incidents are properly documented and addressed, enabling the organization to learn from past incidents and improve its overall security posture. Effective incident response and reporting protocols are essential for maintaining trust and transparency with stakeholders.
Review and Update Procedures
Regular review and update procedures are crucial to maintaining an effective information security policy. These procedures involve periodic assessments of the policy’s relevance, accuracy, and alignment with current threats and technology trends. By conducting regular reviews, organizations can identify gaps or weaknesses in their security framework and implement necessary adjustments or enhancements.
Additionally, updating procedures ensures that the policy remains up-to-date with evolving regulatory requirements and industry standards. Continuous improvement in security measures enhances the organization’s resilience against cyber threats and strengthens its overall security posture, ensuring the ongoing protection of sensitive information.
/powerdms-assets-photos-332-office.jpg?width=996&name=powerdms-assets-photos-332-office.jpg)
Examples of Information Security Policies
Information security policies come in various forms, tailored to meet different organizations’ specific needs and requirements. Common examples include data encryption policies, which outline guidelines for encrypting sensitive information at rest and in transit.
Acceptable Use Policies define permissible ways to utilize organizational resources, including computers, networks, and internet access. Password management policies establish rules for securely creating, storing, and managing passwords.
Incident Response Policies detail protocols for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents. These examples illustrate the diversity of information security policies and their importance in safeguarding organizational assets.
Challenges in Implementing Information Security Policies
Implementing information security policies poses several challenges for organizations. One common hurdle is that employees need more awareness and understanding about the importance of security measures. Resistance to change and organizational culture can also impede the adoption of new policies and procedures.
More resources, both financial and human, may help the implementation of robust security measures. Additionally, keeping pace with rapidly evolving threats and technological advancements requires constant vigilance and adaptation.
Finding the right balance between security and usability could be challenging because stringent regulations could lead to less productive workers. Strong leadership, workforce education, and a proactive strategy for tackling emerging threats in the dynamic cybersecurity landscape are necessary to overcome these obstacles.
Benefits of a Strong Information Security Policy
A robust information security policy offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- It helps safeguard sensitive data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- It fosters trust and confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders, enhancing the organization’s reputation.
- It ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, mitigating the risk of legal penalties and fines.
- It promotes a culture of security awareness among employees, empowering them to protect the organization’s assets.
A robust information security policy strengthens the organization’s resilience against cyber threats and contributes to its long-term success and sustainability.

Conclusion
In conclusion, an information security policy is the cornerstone of a comprehensive cybersecurity framework, providing guidance and direction for safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating cyber risks. By establishing clear guidelines, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing monitoring mechanisms, organizations can proactively protect their digital assets against evolving threats.
Compliance with legal requirements and regular review and update procedures ensure the policy remains relevant and effective in addressing emerging risks. Additionally, funding training and awareness initiatives allows staff members to actively contribute to preserving a safe workplace. A robust information security policy safeguards the company’s integrity and good name while building stakeholder trust and setting the company up for long-term success in today’s ever-changing digital environment.
How often should an information security policy be reviewed?
An information security policy should be reviewed regularly, ideally annually, to ensure its alignment with evolving threats and technological advancements.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with information security policies?
Non-compliance with information security policies can lead to data breaches, legal repercussions, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Who is responsible for enforcing an information security policy?
Enforcing an information security policy is a shared responsibility across all levels of an organization, from leadership to individual employees.
How can organizations enhance employee awareness about information security?
Organizations can enhance employee awareness about information security through regular training programs, simulated phishing exercises, and ongoing communication about emerging threats.








