Introduction to Computers and Information Technology
Unraveling the Basics of Computers and Information Technology
Computers, and information technology are the mainstays of contemporary society, affecting our correspondence, work elements, and worldwide communications. Computers process data and perform tasks, while IT manages data efficiently.
As technology advances and innovations like cloud computing and AI emerge, the IT sector expands, driving growth and reshaping industries. Understanding computers and IT is crucial in today’s digital era, enabling enhanced productivity, connectivity, and collaboration.
Grasping the Nuts and bolts
A PC is a programmable machine that processes information to perform different tasks at its center. Data innovation, then again, incorporates utilizing PCs and programming to oversee and deal with data. From PCs to supercomputers, processing extends, empowering phenomenal headways in different fields.
Significance in Current Culture
PCs and IT drive development, proficiency, and efficiency across ventures in today’s interconnected world. From medical care to funding and diversion to training, every area depends on PCs and IT frameworks to smooth out tasks, examine information, and encourage development.
Advancement of PCs
The advent of PCs traces back to antiquated times, with the innovation of apparatuses like the math device for essential number-crunching computations. Throughout the long term, different developments, such as the mechanical adding machine and punch card frameworks, computers information and technology were ready for the advanced PCs we use today.
Key achievements incorporate the semiconductor’s turn of events, the creation of the chip, and the ascent of individualized computing in the late twentieth century.
From Math devices to Current laptops

Key Achievements in PC Development
From the beginning, a few noteworthy developments have formed the processing direction. The creation of the ENIAC, the leading electronic, broadly applicable PC, proclaimed another time of advanced calculation. Ensuing turns of events, for example, the making of the Internet and the expansion of cell phones, have sped up mechanical advancement.
Principal Ideas in Data Innovation
The principal ideas in data innovation revolve around harnessing the power of data to drive advancements and insights. Data innovation involves strategically using information to create value, solve problems, and make informed decisions.
Key concepts include data analytics, where statistical methods and algorithms uncover patterns and trends, providing actionable intelligence. Another crucial idea is emphasizing data quality and integrity, ensuring accurate and reliable information.
The utilization of advanced technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, plays a pivotal role in extracting meaningful insights from large datasets. Data security and privacy are also fundamental, highlighting the need for robust measures to protect sensitive information. Data innovation aims to transform raw data into valuable knowledge, fostering progress across various sectors and industries.
Information versus Data
Information alludes to crude raw numbers, while data will be handled and coordinated to convey meaning. Data innovation includes gathering, putting away, recovering, and scattering data utilizing different equipment and programming apparatuses.
Hardware and Programming
The hardware integrates the actual pieces of a PC system, including the central dealing unit (microchip), memory, limit contraptions, input/yield devices, and peripherals. Programming suggests the activities, applications, and working structures that enable clients to connect with gear and perform tasks effectively.
Individual Use
From cell phones and tablets to workstations and work areas, individualized computing gadgets have become pervasive, engaging people to remain associated, helpful, and informed no matter where they go. Whether perusing the web, browsing messages, or sharing photographs via online entertainment, PCs have changed how we cooperate with advanced content.
Business Applications
PCs and IT frameworks are crucial in smoothing out tasks, overseeing assets, and working with correspondence in the business world. From stock administration and client relationship management (CRM) programming to cloud-based coordinated effort devices, organizations depend on IT foundations to drive development and gain the upper hand in the commercial center.
Instructive Effect
In school, PCs have changed the learning scene, offering understudies access to information and intuitive learning assets. Innovation has upset how instructors instruct and understudies learn, from digital books and online courses to virtual homerooms and instructive applications, encouraging innovativeness, joint effort, and decisive reasoning abilities.
Data Innovation Framework
The foundation of current IT frameworks lies in a vigorous foundation, including organizations, servers, and server farms, that empower consistent network and information trade.
Organizations and Networks
Organizing advances like the web, intranets, and extranets structure the foundation of current correspondence, permitting clients to trade information and data across huge distances continuously. From wired Ethernet associations to remote Wi-Fi organizations, the advancement of systems administration has worked with worldwide cooperation and data sharing on an extraordinary scale.
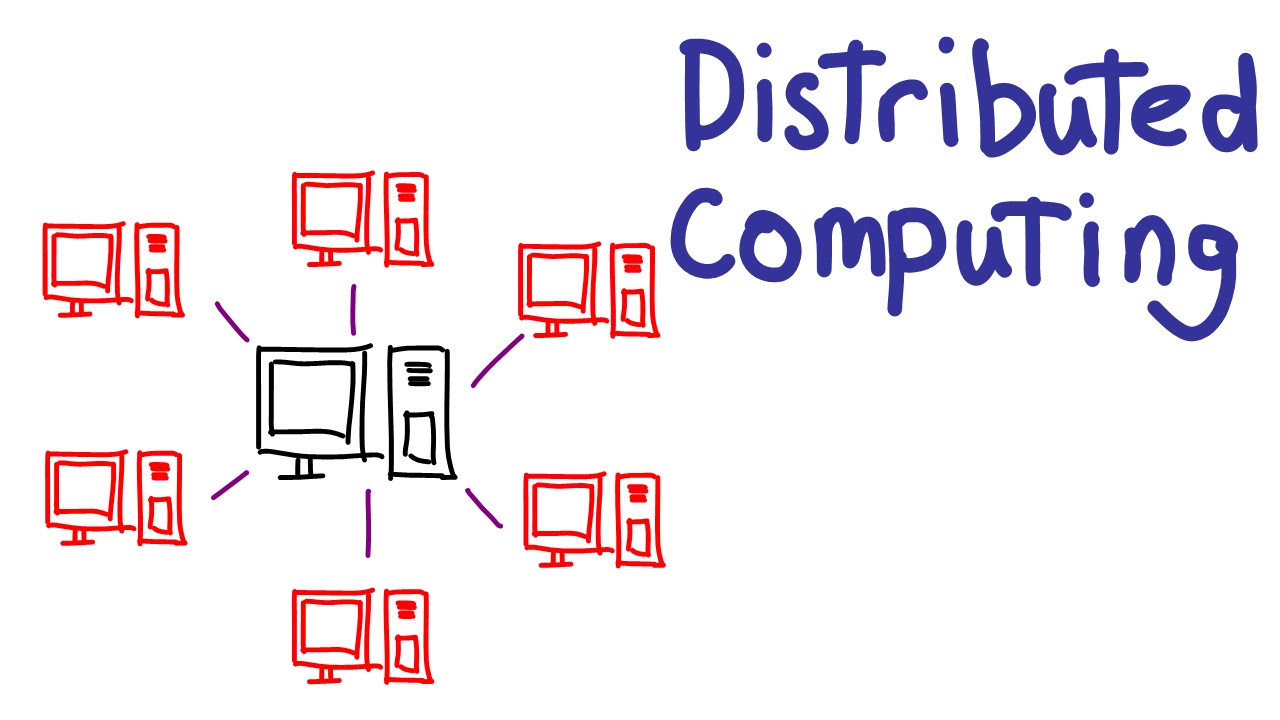
Distributed computing
Distributed computing has emerged as a distinct advantage in the IT framework, offering versatile, on-request access to figuring assets and administrations over the web. From distributed storage and programming as a help (SaaS) to stage as a help (PaaS) and foundation as a help (IaaS), distributed computing has upset how associations send, make due, and scale IT arrangements, driving agility, cost-productivity, and development.
Arising Patterns in Data Innovation
Rising patterns in data innovation (IT) are reshaping the advanced scene, preparing for weighty developments and ground breaking encounters. Artificial brainpower (artificial intelligence) and AI (ML) stand at the front, altering how PCs process information and make decisions.
Computer-based intelligence and ML calculations drive productivity and experiences across ventures, from customized suggestions to prescient investigation. The Web of Things (IoT) is another expanding pattern, associating actual gadgets and empowering consistent correspondence and computerization.
With IoT innovation, intelligent homes, urban communities, and enterprises are becoming more interconnected and influential. Network safety remains an elemental concentration, with progress in danger recognition and counteraction methods to defend computerized resources and protection. As innovation advances, embracing these emerging patterns is critical to remaining ahead in the consistently transforming IT scene.
Artificial consciousness and AI
Computerized reasoning (computer-based intelligence) and AI (ML) address progressive headways in computers, information, and technology. Artificial intelligence mimics human cognitive processes, enabling computers to perform speech recognition and language translation tasks.
Machine learning, part of AI, enables computers to learn without programming. AI and ML technologies are omnipresent daily, from virtual assistants like Siri to recommendation systems on streaming platforms.
They power advancements across businesses, from medical care and money to transportation and amusement, driving proficiency, mechanization, and experiences. As computer-based intelligence and ML develop, they can significantly change how we live, work, and collaborate with innovation.

Web of Things (IoT)
The Web of Things (IoT) alludes to the interconnected organization of gadgets implanted with sensors, programming, and availability that empower them to gather, trade, and follow up on information independently. From brilliant homes and wearable gadgets to modern sensors and shrewd urban communities, IoT innovation is reforming how we communicate with our surroundings, opening new doors for proficiency, manageability, and comfort.
Online protection Difficulties

With the expansion of computerized innovation comes the developing danger of network protection breaks, information breaks, and vindictive digital assaults. Network security, robust defenses, proactive monitoring, and responsive measures are critical as organizations increasingly depend on digital systems for data storage and operations.
The Eventual Fate of PCs and Data Innovation
As we look forward, the fate of computers information, and technology holds gigantic commitment and potential, along with substantial moral contemplations and cultural ramifications.
Forecasts and Theories
Specialists foresee that mechanical advancement will keep speeding up, introducing a period of quantum figuring, expanded reality, and decentralized innovations. With headways in nanotechnology, biocomputing, and quantum cryptography, the limits of what’s conceivable with PCs and IT frameworks are growing dramatically, preparing for disclosures and forward leaps that could reshape humanity’s experiences.
Moral Contemplations
Moral contemplations are vital in innovation, particularly in the consistently developing computer, information, and technology scene. As innovation becomes progressively entwined with our routines, worries about protection, information security, and algorithmic inclination emerge.
Its moral ramifications extend beyond individual protection to cultural effects, including advanced separation and admittance to innovation. Besides, inquiries regarding responsibility and straightforwardness in dynamic cycles emerge as artificial consciousness and AI calculations become more common. People, organizations, and policymakers must proactively address ethical considerations in technology development.
Conclusion
Considering everything, the domain of computers, information, and technology holds huge commitment and potential for molding the fate of humankind. Its effect is evident, from upsetting businesses to changing their daily existence. In any case, with great power comes great responsibility.
As we adopt technological progress, we must prioritize ethics, using innovation to inspire and unite people and organizations, and fostering accountability, transparency, and inclusivity.
2. What are some examples of emerging trends in information technology?
Emerging trends in information technology include artificial intelligence, machine learning, Internet of Things, and cybersecurity.
3. How has cloud computing transformed IT infrastructure?
Cloud computing has revolutionized IT infrastructure by offering scalable, on-demand access to computing resources and services over the Internet.
4. What are some ethical considerations in the field of information technology?
Ethical considerations in information technology include privacy concerns, data governance, digital divide, and algorithmic bias.
5. What does the future hold for computers and information technology?
The future of computers and information technology holds tremendous promise, along with significant ethical considerations, as we embrace emerging technologies and navigate the complexities of the digital age.