What is a Web Browser | Its Functions, Types & Questions
Internet Basics: Using a Web Browser
A Web Browser Functions Explained takes you anywhere, allowing you to see text, pictures, and video from anywhere.
Firefox Privacy Notice
 The web is a vast and powerful tool. Every day, it affects how we work, play, and collaborate. Depending on how it’s utilized, it spans countries, drives trade, sustains connections, drives the development motor representing things to come, and is liable for more images than we understand how to manage.
The web is a vast and powerful tool. Every day, it affects how we work, play, and collaborate. Depending on how it’s utilized, it spans countries, drives trade, sustains connections, drives the development motor representing things to come, and is liable for more images than we understand how to manage.
Everyone must have access to the web, but it’s also vital that we all understand the tools we use to access it. We dependably use internet browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Apple Safari, yet do we see the value in what they are and how they work? In a short period, we’ve gone from being confounded by the ability to email someone worldwide to changing our point of view of information. It’s anything but an issue of the amount you know any longer, but just an issue of what program or application can get you to that data quickly.
In a short period, we’ve gone from being amazed by the capacity to email somebody all over the planet to adjusting our opinion on data.
How does a web browser work?
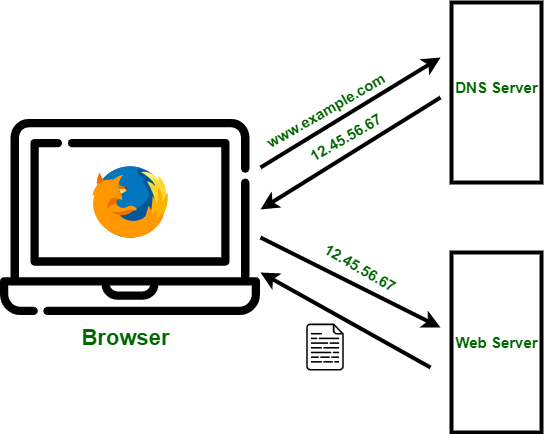
A Web Browser Functions Explained takes you anywhere on the Internet. It retrieves information from other parts of the web and displays it on your desktop or mobile device. The data is moved utilizing the Hypertext Move Convention, which characterizes how text, pictures, and video are sent on the web. This data should be shared and shown in a predictable configuration so that individuals utilizing any program can see it anywhere on the planet.
Sadly, not all browser makers choose to interpret the format in the same way. For users, this means that a website can look and function differently. Creating consistency between browsers so that any user can enjoy the Internet, regardless of their browser, is called web standards.
When the web browser fetches data from an internet-connected server, it uses software called a rendering engine to translate that data into text and images. This data is written in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), and web browsers read this code to create what we see, hear, and experience on the Internet.
Hyperlinks allow users to navigate to other pages or sites on the web. Every webpage, image, and video has its unique Uniform Resource Locator (URL), also known as a web address. When a program visits a server for data, the web address tells the program where to search for all that is depicted in the HTML, which then tells the program where it goes on the page.
Cookies (not the yummy kind)
Websites save information about you in files called cookies. They are saved on your computer the next time you visit that site. Upon your return, the website code will read that file to see that it’s you. For example, when you go to a website, the page remembers your username and password – that’s made possible by a cookie.
Some cookies remember more detailed information about you. Your interests, your web browsing patterns, etc. This means a site can provide more targeted content – often in ads. Some types of cookies, called third-party cookies, come from sites you’re not even visiting and can track you from site to site to gather information about you, which is sometimes sold to other companies. Sometimes, you can block these cookies, though not all browsers allow you to.
In a short period, we’ve gone from being stunned by the capacity to email somebody all over the planet to adjusting our opinion on data.
When you go to a site, and the page remembers your username and secret phrase, that is made conceivable by a treat.
Understanding privacy
Nearly all major browsers have a private browsing setting. These hide the browsing history of different clients on a similar PC. Many believe that private perusing or undercover mode will conceal their personality and perusing history from network access suppliers, legislatures, and promoters. They don’t. These settings clear your system’s history, which helps deal with sensitive personal information on a shared or public computer. Firefox goes beyond that.
Types of Web Browsers
There are several web browsers, each with exceptional elements and capacities. The most famous include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Safari. These programs vary in viewpoints like speed, UI, and compatibility with different gadgets and working frameworks. For example, Google Chrome is famous for its speed and broad library of enhancements.
Key Features of Modern Web Browsers
Modern web browsers offer a plethora of features that enhance the user experience. A pivotal part of these programs is their UI, which usually incorporates a location bar, bookmarks, and tabs. Tabs allow clients to open various pages simultaneously without jamming their screens, making performing multiple tasks much more straightforward.
Choosing the Right Web Browser for You
Selecting the right Web Browser Functions Explained relies upon different elements, including speed, security, similarity, and individual inclination. For instance, expecting that you’re overwhelmingly placed assets into the Google natural framework, Chrome might be the best choice given its steady compromise with other Google organizations like Gmail and Google Drive. Then again, expecting security is your fundamental concern. Mozilla Firefox is known for its solid areas of client data protection.

Another aspect to consider is the availability of extensions and add-ons, which can improve your perusing experience.
Conclusion
A Web Browser Functions Explained is a critical device in our computerized lives, empowering us to access and connect with the immense resources of the web. Understanding what an internet browser is, how it works, and the various choices available can assist you with making a decent decision that best suits your needs. Whether you’re zeroing in on speed, security, or comfort, there’s a program for everyone.
Could I utilize various internet browsers on one gadget?
Indeed, you can introduce and utilize numerous programs on a similar gadget, which can be valuable for various errands or inclinations.
For what reason is my internet browser running gradually?
Browser performance can be affected by a variety of factors, such as having too many tabs open, using outdated software, or relying heavily on extensions. Understanding these factors can help you identify and address any issues that may be slowing down your browser.